What is D.C. Motor
Definition of D.C. Motor:
It is an electrical machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy . This electric motors can be operated by giving both AC current and DC current .
Principle Of D.C. Motor:
Definition of D.C. Motor:
It is an electrical machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy . This electric motors can be operated by giving both AC current and DC current .
- It has input and output terminals . Input treminals are connected to electric current and mechanical energy is collected from output terminals .
- It works on the princple of Faradays laws of electromagnetic induction .
Principle Of D.C. Motor:
A machine that converts d.c. power into mechanical power is known as a d.c. motor. Its operation is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, the conductor experiences a mechanical force. The direction of this force is given by Fleming’s left hand rule and magnitude is given by;
F = BIl newtons
Basically, there is no constructional difference between a d.c. motor and a d.c.generator. The same d.c. machine can be run as a generator or motor.
Working Of D.C.Motor:
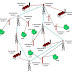
Consider a part of a multipolar d.c. motor as shown in Fig. When the terminals of the motor are connected to an external source of d.c. supply:
(i) the field magnets are excited developing alternate N and S poles;
(ii) the armature conductors carry ^currents. All conductors under N-pole
carry currents in one direction while all the conductors under S-pole
carry currents in the opposite direction.
Suppose the conductors under N-pole carry currents into the plane of the paper and those under S-pole carry currents out of the plane of the paper as shown in Fig.(4.1). Since each armature conductor is carrying current and is placed in the magnetic field, mechanical force acts on it.Referring to Fig. and applying Fleming’s left hand rule, it is clear that force on each conductor is tending to rotate the armature in anticlockwise direction. All these forces add together to produce a driving torque which sets the armature rotating.
When the conductor moves from one side of a brush to the other, the current in that conductor is reversed and at the same time it comes under the influence of next pole which is of opposite polarity. Consequently, the direction of force on the conductor remains the same.
What is Principle of D.C. Motor
4/
5
Oleh
Unknown