RECIPROCITY THEOREM:
In a linear, passive and bilateral network, the ratio of responce to excitation is constant even though the source is interchanged from input terminals to output terminals.
i.e., I/V =Constant
I1/V1=I2/V2
Properties of Reciprocity Theorem:
Explanation of Reciprocity Theorem:
The location of the voltage source and the current source may be interchanged without a change in current. However, the polarity of the voltage source should be identical with the direction of the branch current in each position.
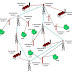
The Reciprocity Theorem is explained with the help of the circuit diagram shown below
The various resistances R1, R2, R3 is connected in the circuit diagram above with a voltage source (V) and a current source (I). It is clear from the figure above that the voltage source and current sources are interchanged for solving the network with the help of Reciprocity Theorem.
The limitation of this theorem is that it is applicable only to single source networks and not in the multi-source network. The network where Reciprocity theorem is applied should be linear and consist of resistors, inductors, capacitors and coupled circuits. The circuit should not have any time-varying elements.
In a linear, passive and bilateral network, the ratio of responce to excitation is constant even though the source is interchanged from input terminals to output terminals.
i.e., I/V =Constant
I1/V1=I2/V2
Properties of Reciprocity Theorem:
- Reciprocity theorem is applicable only for linear, passive and bilateral networks, i.e. networks with R,L,C and Transformer as element, so called Reciprocal Networks.
- The precence of the dependent sources makes the network active and hence the reciprocity theorem is not applicable, so called the Non Reciprocal network
Explanation of Reciprocity Theorem:
The location of the voltage source and the current source may be interchanged without a change in current. However, the polarity of the voltage source should be identical with the direction of the branch current in each position.
The Reciprocity Theorem is explained with the help of the circuit diagram shown below
The various resistances R1, R2, R3 is connected in the circuit diagram above with a voltage source (V) and a current source (I). It is clear from the figure above that the voltage source and current sources are interchanged for solving the network with the help of Reciprocity Theorem.
The limitation of this theorem is that it is applicable only to single source networks and not in the multi-source network. The network where Reciprocity theorem is applied should be linear and consist of resistors, inductors, capacitors and coupled circuits. The circuit should not have any time-varying elements.
What is Reciprocity Theorem
4/
5
Oleh
Unknown